In this guide we’ll cover:
- What is Google Trends
- How to use Google Trends
- COVID-19 and Google Trends
- Practical applications for Google Trends
What is Google Trends?
If you have never heard of or used Google Trends before then you are in for a treat! Google Trends is a tool that allows you to compare the popularity of search terms and trends. With a number of different features, it allows you to gain an understanding of the hottest search trends of the moment along with those developing in popularity over time.
How to use Google Trends
Well, the good news is Google Trends is free! It’s open for anyone to use, whenever you like. Simply navigate to Google Trends and you’ll see the dashboard. From here you can either navigate around the trending stories or enter topics into the search box:
Google Trends has a tonne of different filters you can explore this data with including:
- Country, Region, City
- Dates – hourly, day, month, year, 2004 onwards
- Categories e.g. Arts, Science, Sports
- Type of search – Web, Image, Shopping, News, YouTube
COVID-19 and Google Trends
Before we jump into some of the more traditional applications for Google Trends, it wouldn’t be a 2021 blog without mentioning the impact of COVID-19. With traditional search volumes from third-party tools relying on a 12-month average, we can throw many of them out of the window during this pandemic. People in lockdown, the shift of interests and the migration to digital has meant that us marketers have had to adapt our strategies.
This makes Google Trends is an even more useful tool. An example of this would be if you’re involved in the fitness industry. Let’s take ‘exercise bike’ as a search term.
The search volume you see in a third-party tool might indicate a search volume that is out of date. Whereas, in Google Trends you can see the growth in interest, see below.
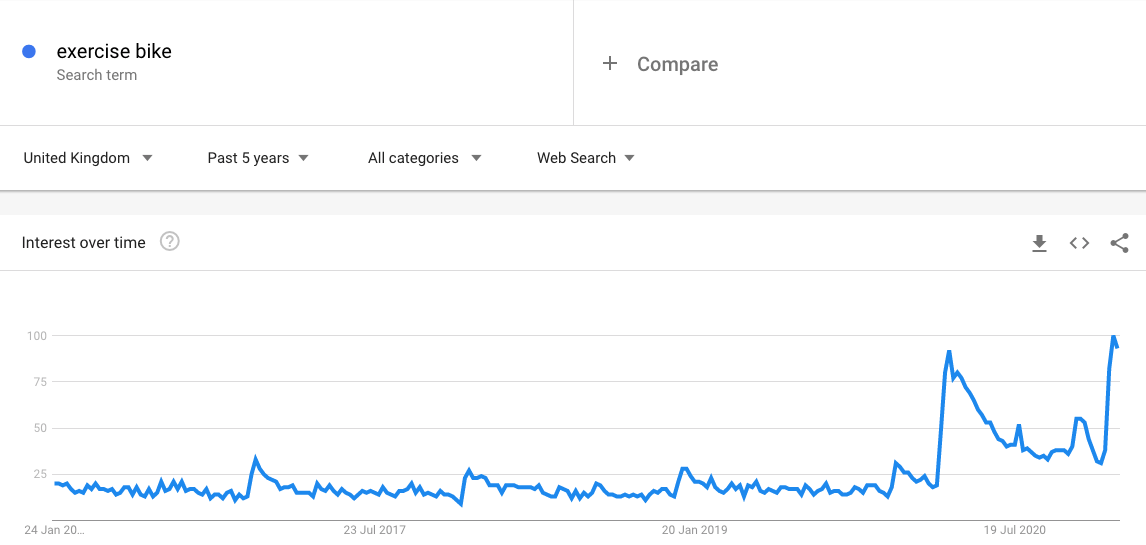
Note: Google Trends data is not search volume data you might see in Google Keyword Planner but the relative popularity of a search query.
If you relying solely on search volume data you may be behind the curve for understanding which of your products are the most popular, which you should be investing in building out their pages and which you should be pushing with ads.
If you’re not already, you should be integrating Google Trends data into your keyword research and content plans to stay agile and adapt to what your audience wants.
How else does Google Trends help?
In September 2020, Google themselves made its data on search trends to do with COVID-19 symptoms public. The data was primarily made up of the volume of searches of over 400 symptoms, signs, and health conditions. The aim – too effectively track the spread of disease through users search terms.
Critics argue that Google Trends data shouldn’t be relied upon as it does not always match up to the real-world data. Still, Google Trends data is another data source and tool we can use to fight the pandemic.
If you’re interested in reading more and keeping up to date with search insights from Google Trends, check out their collection of articles here.
What can I use Google Trends for?
Right, let’s get to business. The list of potential uses for Google Trends is endless, but here is a quick step by step guide to using Google Trends to benefit your business.
- Understanding your audience
- E-commerce product keyword research
- Identifying seasonal trends
- Brand awareness activity
- Big data, advanced targeting
- Spotting trending topics
- Use it for fun!
1. Understanding your audience
As the most popular search engine, Google has become more of an institution than a search engine. This allows their search data to be incredibly indicative of public opinion and interests. You can use this to your advantage by understanding public opinion related to your industry.
If I were using Google Trends for Hallam I would like to know how the perception of our industry has changed over time and where it lays now.
I would get myself on Google Trends and start with the basics. I would type some key phrases in the search box above that I think would be indicative of a difference in opinion and understanding of our industry as per the below screenshot:

You will now be greeted with a graph which will show you the search trends over time for these phrases compared to each other.
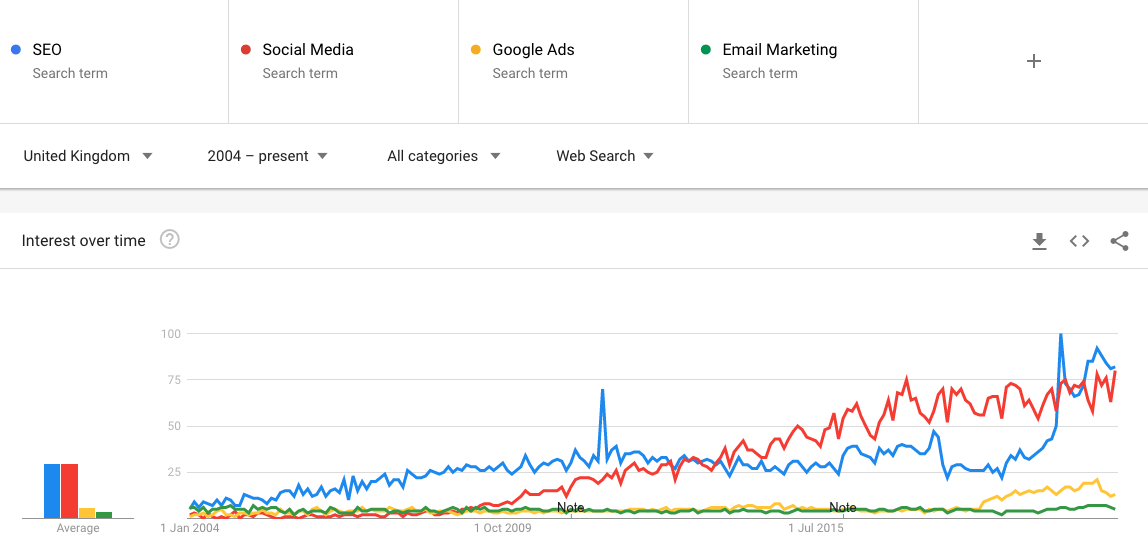
From this graph, I can see how trends have massively changed since 2004. What is particularly striking is the rise of social media (red), overtaking all other channels towards the end of 2013 – right up until March 2020. However, during the first lockdown, we saw a huge shift to digital and therefore an expected rise in SEO as a search term, more so than Google Ads and even Social Media.
2. Use Google Trends to find products for your eCommerce website
You can use Google Trends to help you find ideas for products to sell on your eCommerce website, or perhaps even to help you come up with a new retail business idea.
Let’s say I want to set up a website selling virtual reality headsets in the UK. I’d enter some variations of product terms into Google trends and select the option to show data from the United Kingdom since 2004. Here I searched for ‘VR headsets:
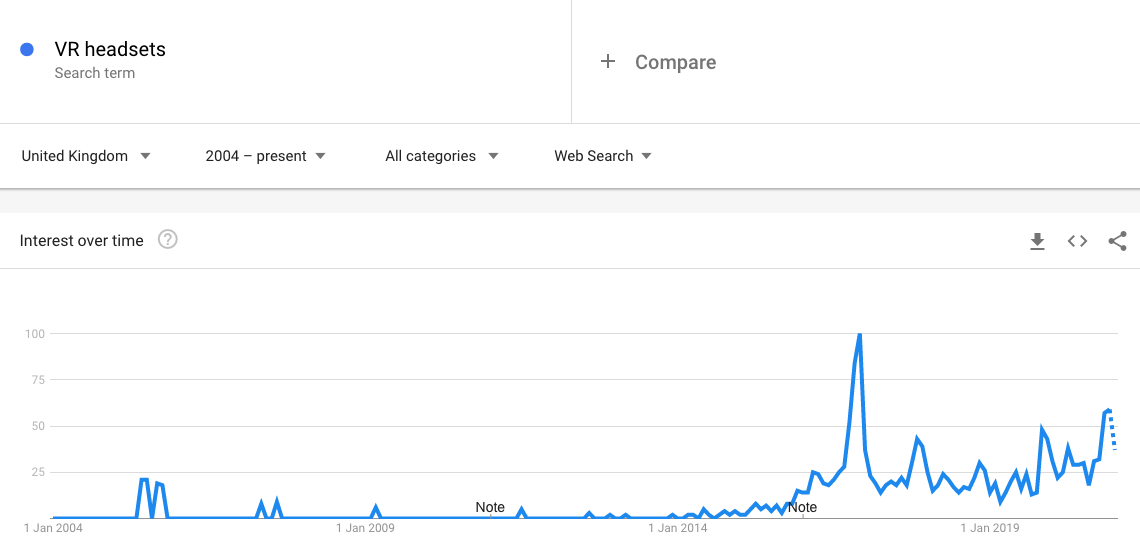
As you can see, the search volume has been quite low before a big spike in Dec 2016 before levelling out since then. This data tells me that the initial clamour for VR headsets was very high but it has settled down since then. I’d probably consider such products to be a good investment for my business but keep an eye on the technology developing further before making it the core of my business.
3. Identify seasonal trends
You can also use Google Trends to help you identify seasonal peaks in your industry. Say, for example, you want to sell food hampers:
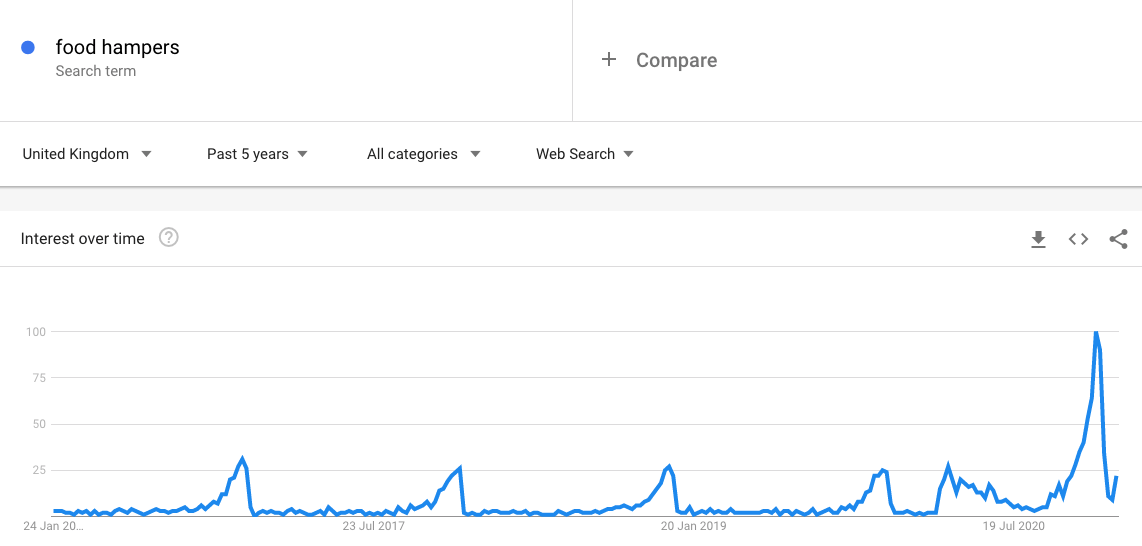
This trend graph shows what you’d expect from a traditional year – a huge spike in interest around December. However, we can see that interest actually starts to pick up around July/August, which indicates that I should start marketing activity earlier in the year to ensure I remain competitive.
In 2020, we saw a massive spike during the first lockdown in March. No surprises there with the majority of transactions moving online. The December peak is unlike anything we’ve seen over the past 5 years too – it looks like plenty of people received food hampers for Christmas.
1 step further
You could also take your research, or product development, further and use the ‘related topics’ section to identify types of food hampers:
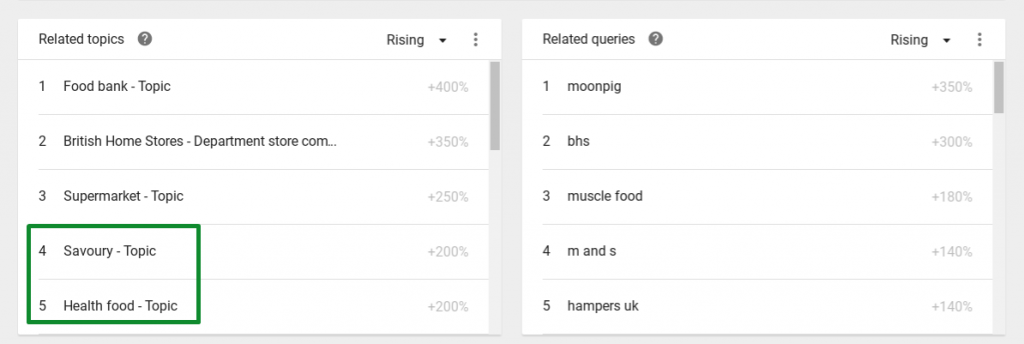
Here we can see that ‘savoury’ and ‘health food’ searches are gaining interest, which I’d see as an opportunity to launch ‘The Ultimate Healthy Eating Christmas Hamper’ or a ‘Savoury Favourites Hamper’!
The related topics section is really useful for you to understand the type of user journey your customer might be on, what topics they are also searching for and when.
What about amplification?
The seasonality information you can get from Google Trends is fantastic for creating content calendars. Your content amplification plans can centre around these peaks so make sure your social and outreach tactics match up to what you’re seeing in Google Trends.
Another example of this is ‘Blue Monday’. This is the name given to the third Monday of January. Coined as the most depressing day of the year due to the return to work, weather and distance to next Christmas – it would be silly for you to produce and amplify content around this topic at any other point of the year.
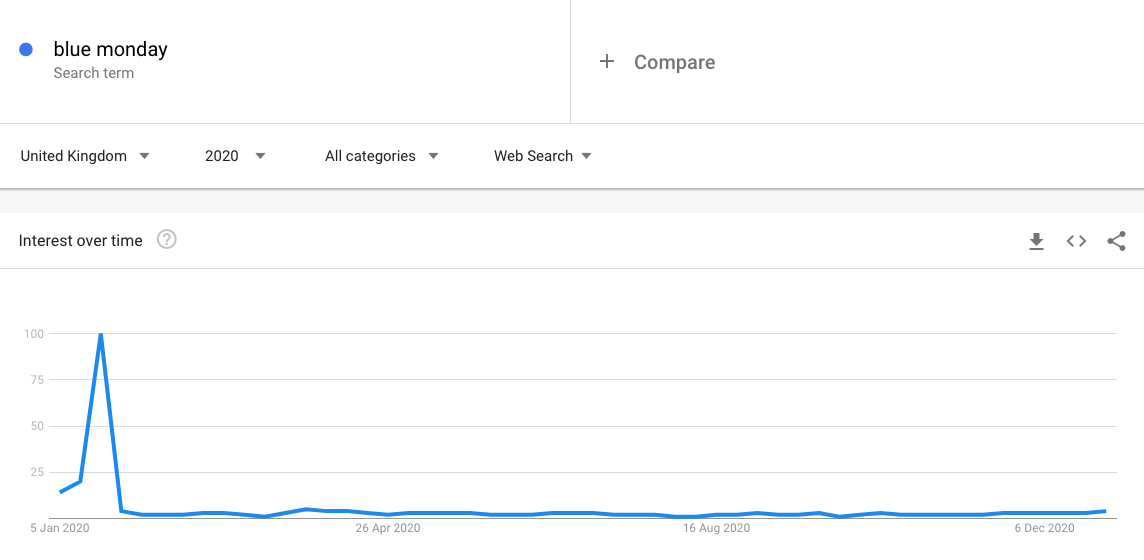
4. Brand awareness activity
Most marketers will tell you that one of the hardest tasks we can do is to track and monitor the results of brand building activity. It’s essential for every business to invest in, but it can often be hard to justify to the decision-makers in the business as it doesn’t have the ‘money in – money out’ nature of sales activation activity.
There are a couple of metrics you can measure including Share of Voice and Brand Penetration – but one of the easiest and most effective ways is to use Google Trends.
I’ll be using some of my closest lockdown 3.0 friends as an example here. If we enter in ‘Brewdog’, a brewing company that invests heavily in brand activation activity, we can see how the brand has grown over the past 5 years.
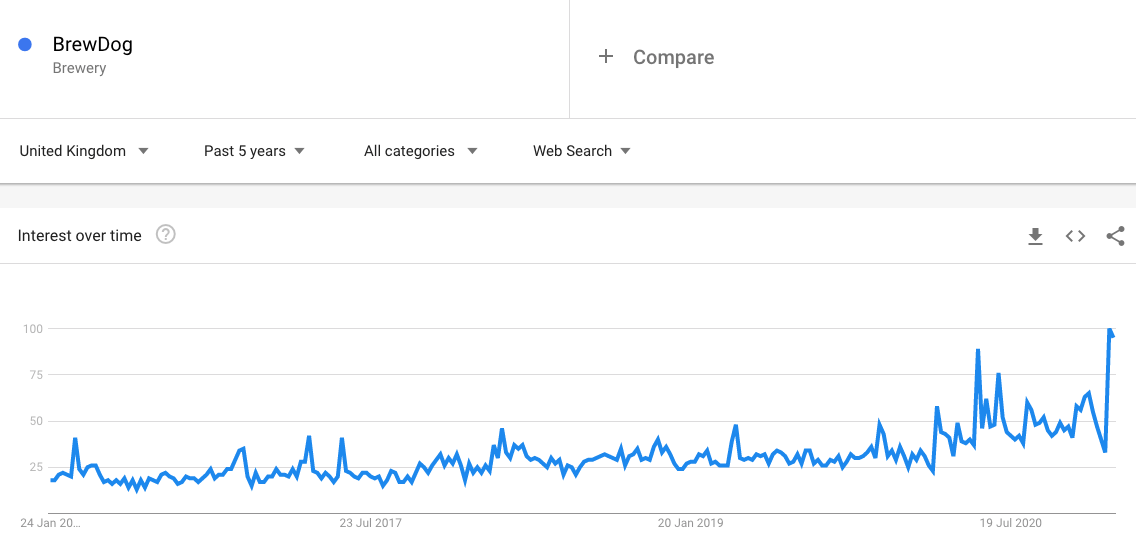
You can also use this for assessing yourself against your competitors.
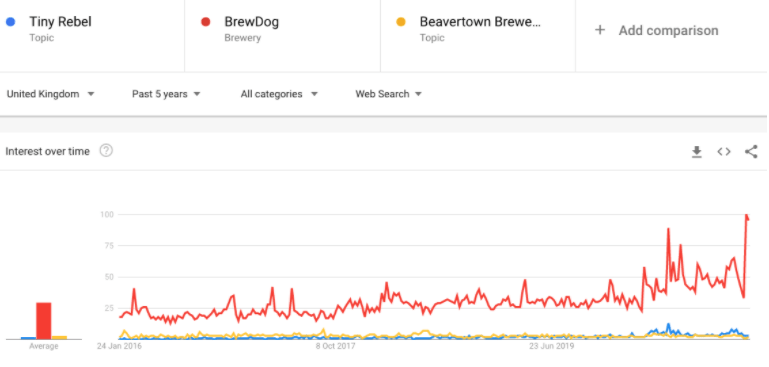
Looking at the data you can ask yourself
- Is your competitor’s brand growing or shrinking?
- Has yours been stagnating for years?
- Where do you fit in the wider ecosystem?
- Are they more popular in certain areas of the world?
- Are they more popular in Google Shopping, Image Search?
- Has your competitor’s content gone viral in Google News?
There are plenty of insights and opportunities to explore with this data and it’s totally free! Importantly, it’s data like this that will be a game-changer next time you’re attempting to secure resource for essential brand activation activity.
5. Big data, advanced targeting
As we mentioned at the start of the blog, there are many filters and more advanced targeting methods you can apply to Google Trends. For example, if I was setting up a hybrid car showroom, I’d want to know where the most interest in the product would be. Where would I make the most money?
Looking at Google Trends for the US, it indicates that the west coast and northeast of the country show the most relative interest in the search term ‘hybrid car’
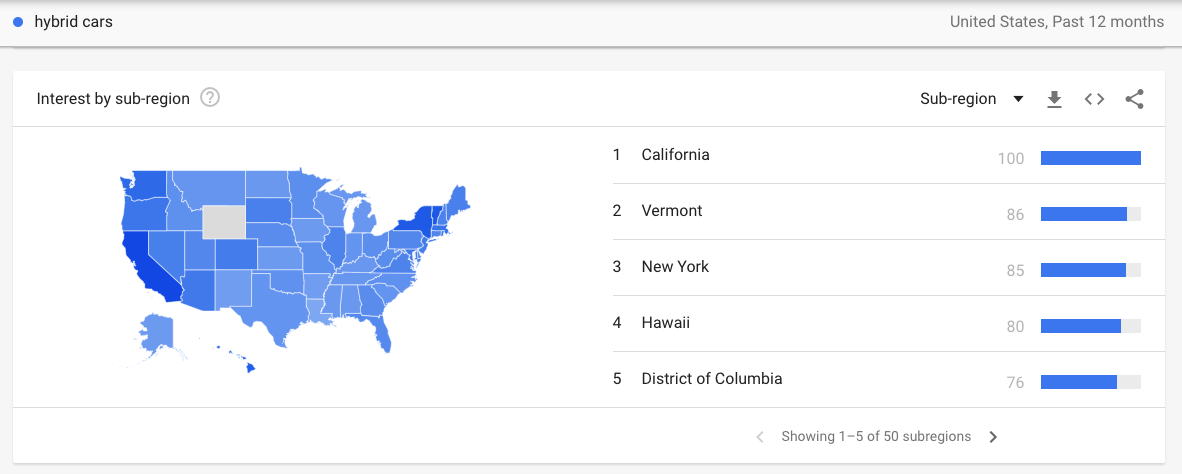
That still seems quite broad
Do not fear, your data can be even more granular, adding metro and city filters to your search term.
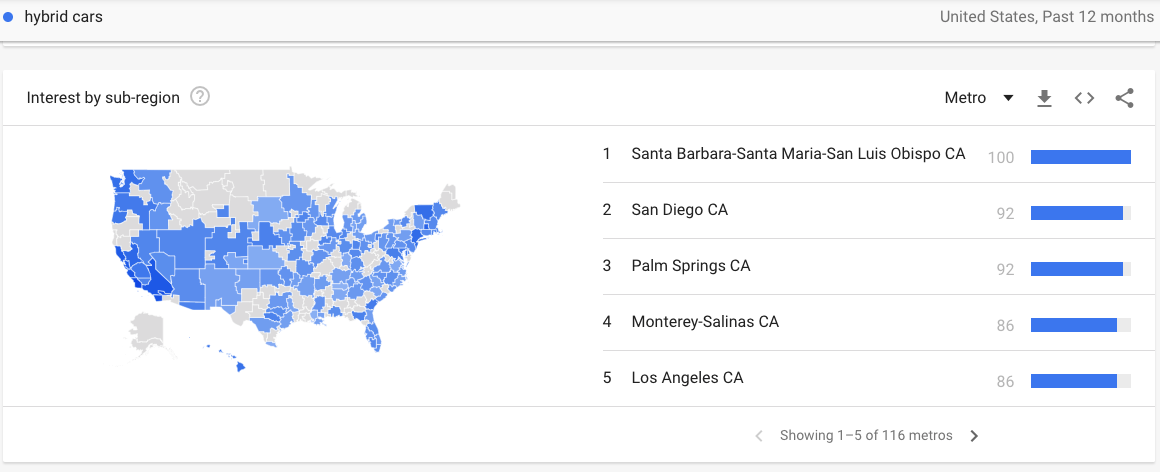
What can I do with this information?
If you’re a national supplier you can target these areas with paid media ads or explore opening a showroom there. If you’re not keen on investing money into ads, you can create targeted content or social posts specifically to these regions.
6. Spotting trending topics
The trending searches area of Google Trends is always interesting. We can see Daily Search Trends, Real-Time Search Trends and filter it all by location. So, what’s trending in the UK today?
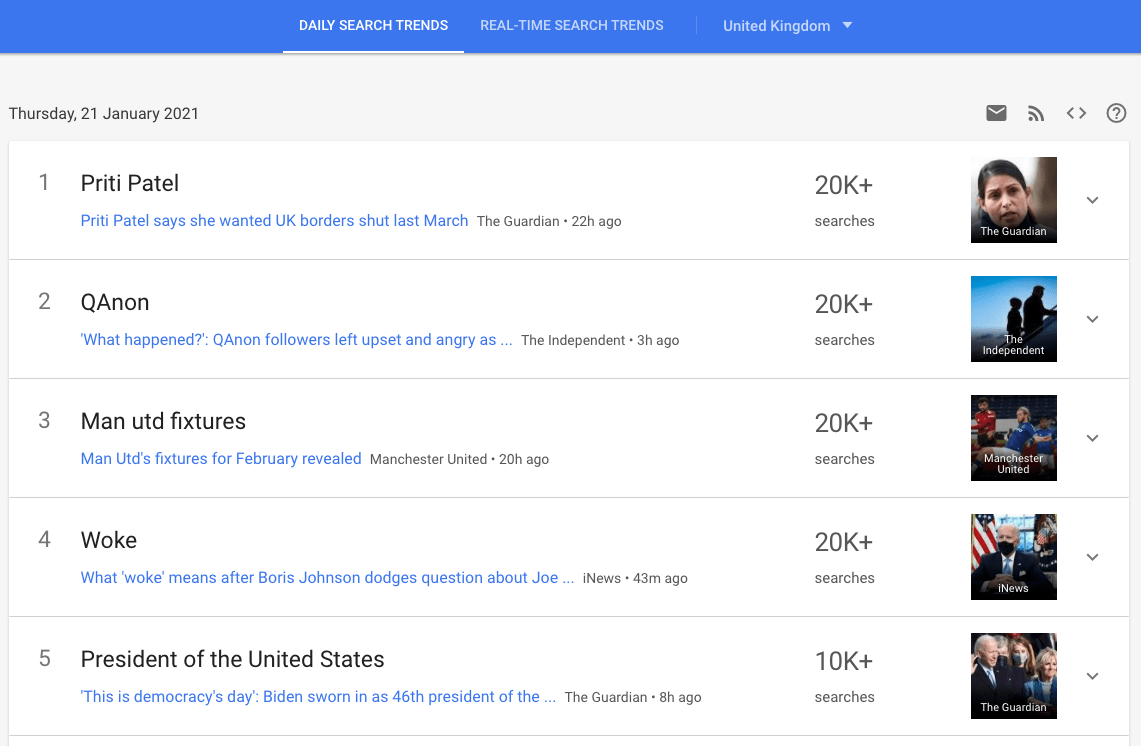
With Joe Biden’s inauguration taking place on the 20th January it makes sense that he would be trending. We can also see Priti Patel trending around the border debate from March. This section is great for understanding the biggest topics in your country. In terms of what you can do with this, I’d recommend integrating this into your agile newsjacking strategy. If you’re after a guide to this, and FREE template, PR consultant Rebecca Peel has written everything you need to know about newsjacking.
You can produce timely and relevant content on trending topics or provide expert comment to gain publicity, links and build your thought leadership.
7. Use it for some fun!
Lastly, you can use Google Trends for a bit of fun or just to confirm some of your suspicions about trends in your industry.
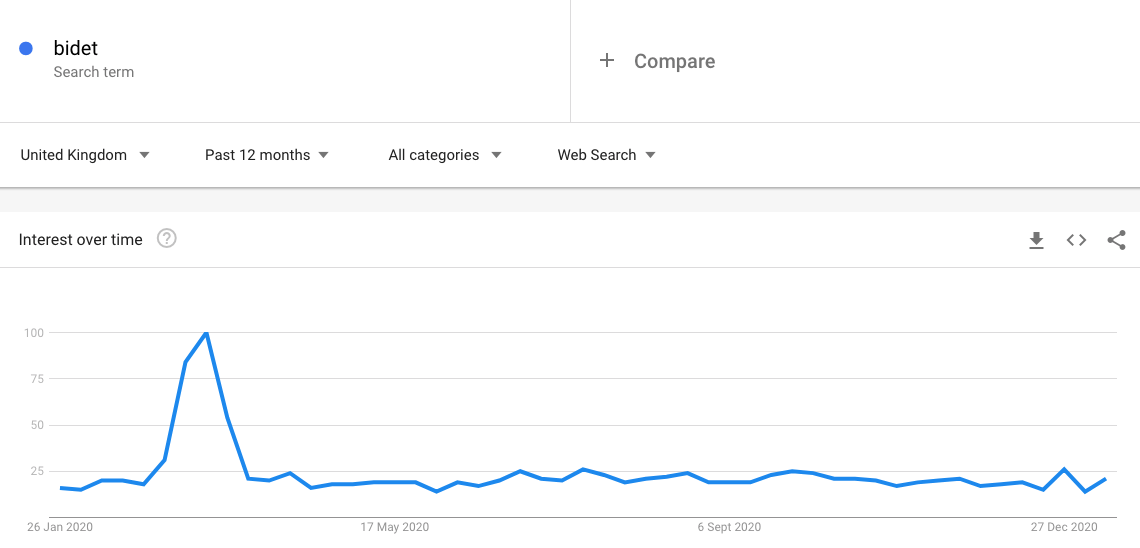
The first lockdown saw a mad rush for toilet paper and many individuals unnecessarily hoarding. Unsurprisingly, if you look at the interest in ‘bidets’ you’ll see a huge spike at the end of March!
Final thoughts
We all know that great, relevant and popular content is key to a digital strategy and SEO success. The key to popular content is relevance and timing. Searching around Google Trends is a great way to understand what people are talking about, what they are interested in. More importantly what kind of content they are going to enjoy and when they will enjoy it most.
As a free tool, it’s really unparalleled for the type of data it gives a marketer. If you haven’t added it to your swiss army SEO toolset, you really should – even if it’s just for a bit of fun!



